Giving your machines, 3D machine vision technology is like changing the way your machines understand and react to their surroundings. Think of your machines being able to see and sort objects in 3D, just like we do, but faster and without mistakes. This tech can make a big difference in how smoothly and efficiently your production line runs.
If you want to make your manufacturing process better, learning about 3D machine vision is a must. Here’s how it can change the game for you.
What is a 3D Vision System?
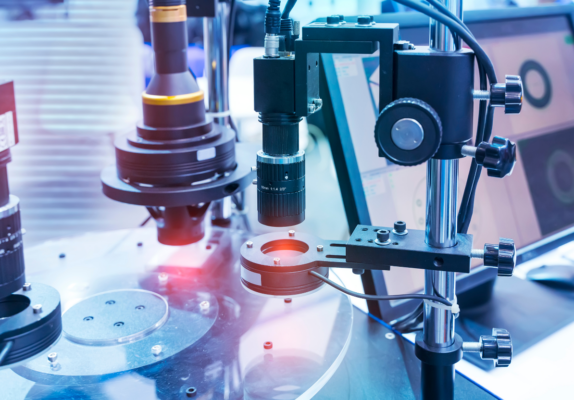
3D machine vision is like giving your machines superpowers to see in 3D, just like us. This tech captures images from different angles using cameras and sensors. Then, it uses software to combine these images into a 3D model. This is big news for your production line because it means machines can now spot defects, measure objects, and guide robots with amazing accuracy.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what makes it tick:
- Cameras and Sensors: These are the eyes. They snap pictures from various angles.
- Lighting: It’s all about making sure those pictures are crystal clear, without any tricky shadows or glare.
- Software: This is the brain. It takes those pictures and turns them into a 3D model that the machine can understand and act on.
Getting the hang of these components is your first step towards transforming your manufacturing process. With 3D machine vision, you’re not just upgrading your tech; you’re customizing it to solve your unique challenges. Whether you’re checking the smallest parts or managing complex assemblies, this technology tailors itself to boost your efficiency like never before.

What is the Difference Between 3D Vision & 2D Vision?
In the world of machine vision, you’ll come across two main types: 3D and 2D vision. Both play very different roles on your manufacturing line. Understanding the difference can help you pick the right tool for your job.
2D vision is like a classic photograph. It captures flat images with length and width but no depth. This is perfect for simple tasks where you just need to check the appearance of a product, like scanning barcodes or verifying labels. It’s straightforward and effective for many applications.
On the other hand, 3D vision not only sees the length and width but also measures the depth of objects. This depth perception allows your machines to understand the shape, size, and position of objects in a way 2D vision can’t. It’s crucial for more complex tasks, such as inspecting the volume of a product, guiding robots for assembly, or sorting objects based on their size.
Here’s a quick rundown:
- 2D Vision: Great for surface-level tasks. It’s like having a snapshot of the top view.
- 3D Vision: Adds depth to the picture. It lets your machines grasp the full shape and size of objects.
Choosing between 3D and 2D vision depends on your specific needs. If your goal is to ensure a label is correctly placed or a part is present, 2D vision might be all you need. But, if you’re looking to accurately place parts in an assembly or check the volume of a product, 3D vision is your go-to.
How Does a 3D Vision System Work?
Here’s a quick guide to how it all comes together.
It starts with cameras and sensors—your machine’s eyes. These don’t just snap a single flat photo. Instead, they take multiple shots from different angles to get a full view.
Lighting is crucial, too. It ensures each image is clear, without shadows or blurs, so the system can accurately understand the scene.
The real magic is in the software. Think of it as the brain that stitches those multiple images into one 3D model. This isn’t just for show. This model lets your machine grasp the exact size, shape, and location of objects.
Imagine a robot arm that needs to pick up a part. With 3D vision, it knows precisely where the part is, how it’s angled, and even if it’s upside down. This means the robot can adjust and pick it up right every time, making your production faster and less prone to errors.
So, in simple terms, a 3D vision system captures various images, uses spot-on lighting for clarity, and then the software builds a 3D model. This model is what helps your machines perform tasks with incredible accuracy. It’s a must-have for boosting your line’s speed and precision.
Average Costs & ROI When Investing in 3D Machine Vision:
When you’re thinking about adding a 3D vision system to your manufacturing line, it’s a big decision with a price tag ranging from $5,000 to $20,000. This cost includes everything you need to get started, like the hardware and software, and even covers ongoing needs like data processing and storage. Thanks to newer, smarter technologies, especially those that use AI, the cost of these systems has actually gone down, making them more affordable than you might think.
3D vision systems are a step up from traditional 2D ones because they can deal with problems like parts not lining up correctly, shiny reflections, or colors blending together. They work by either projecting patterns of light onto objects or using lasers to measure them, making sure every inspection is spot-on. This tech can be tailored to fit exactly what you need, whether that’s checking tiny details or making sure parts move through your line without a hitch.
In the end, the money you put into a 3D vision system can pay off by making your operations smoother, reducing waste, and ensuring your products meet high standards. While the upfront cost might seem high, the boost in productivity and savings on waste and manual inspections can quickly balance out the initial investment.
5 Key Advantages of 3D Vision Systems:
3D vision systems offer incredible benefits that make machines and robots work smarter and more accurately. Here are five key advantages for you:
1. See Depth Clearly:
3D systems measure how far away objects are. This helps machines precisely grab, move, or build things, just like you’d carefully place a cup on a shelf.
2. Better Object Spotting:
These systems recognize objects from all angles, making it easier for machines to pick up a tool or a toy from a pile, much like finding your favorite book in a stack.
3. Works Anywhere:
Whether it’s bright or dim, indoors or outside, 3D vision keeps working perfectly. It’s like having night vision goggles that also work in the daylight.
4. Flexible for Many Tasks:
From checking if a product is made right to helping robots move around obstacles, 3D vision is a jack-of-all-trades, adapting to many different jobs.
5. Avoids Mistakes:
With its detailed view, 3D vision helps robots avoid errors, like not missing a spot when painting or ensuring a part fits just right, similar to how you’d double-check your work on a project.
These advantages make 3D vision systems a powerful ally in automation, helping machines see and interact with the world more like humans do.
Applications:
3D vision systems have many uses in different jobs, like robot navigation, recognizing objects, checking things, and putting stuff together. Here are some common examples:
1. Robot Navigation:
These systems help robots “see” in 3D, so they can move around tricky places and avoid obstacles. It’s handy in tasks like warehouse work, where robots need to dodge things and find their way.
2. Object Recognition & Tracking:
3D vision helps robots spot and follow objects, which makes them better at interacting with things. It’s useful in jobs like sorting and packing, where robots need to identify and pick up items.
3. Inspection & Quality Control:
These systems are great at checking things for problems. For instance, they can measure the size of something we make or find mistakes in a finished product.
4. Assembly Tasks:
3D vision helps guide robots and other machines as they put things together. For example, it can help line up parts and make sure they’re in the right place.
3D vision systems are flexible and strong tools that boost the performance and reliability of robots and other machines. They find use in various industries, like manufacturing, shipping, and healthcare.
Common Industries That Utilise 3D Vision:
3D vision systems find use in many industries, like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and more. Here are some examples:
1. Manufacturing:
They’re often used in manufacturing to check product dimensions and help with assembly. For instance, they can make sure a manufactured part is the right size and in the correct spot during assembly.
2. Logistics:
In logistics, 3D vision systems help robots and automated systems move around warehouses and handle objects better. This makes tasks like picking and placing stuff more efficient.
3. Healthcare:
In healthcare, these systems assist with medical procedures, like surgery and imaging. They can guide robotic surgical tools or create 3D body images for diagnoses.
4. Retail:
In retail, 3D vision systems aid in tasks such as sorting and packing products. They help robots identify and follow objects, so they can pick and place them more accurately.
In general, 3D vision systems are valuable in many industries, and they significantly boost the performance and reliability of robots and other automated systems.
How to Choose the Right 3D Vision System?
When you’re picking a 3D vision system, you need to think about a few things. The accuracy and resolution of the cameras matter, so does the software, and if it suits what you want to do. Here’s how to choose the right one:
1. Know What You Need:
First, figure out exactly what you need from the 3D vision system. This will help you understand what features and abilities it should have and compare your options better.
2. Camera Quality:
The accuracy and resolution of the cameras are super important. They affect how good the images are and how well the system works. Usually, higher accuracy and resolution mean more detailed 3D images, but they can also be pricier.
3. Software & Algorithms:
The software and algorithms used to handle the camera images are also a big deal. Look for systems that use advanced techniques like deep learning to get more information from the images and make the system work better.
4. Suitability for Your Needs
Think about whether the 3D vision system works for your specific task. If it’ll be in a tough environment, make sure it’s sturdy. If it needs to work super fast, look for one with a quick frame rate and low delay.
To sum it up, choosing the right 3D vision system means checking out your options and seeing if they match what you need. By following these steps, you can get a system that does the job well and is worth the investment.
Conclusion:
To sum up, 3D vision lets your machines see in 3D, making them smarter and more precise. It combines pictures from different angles to create a full picture, helping your machines spot, sort, and check objects better. This tech is great for complex jobs where details matter. If your work needs more than just a simple look at things, like making sure parts fit perfectly in assembly, 3D vision is what you need. It’s a big step up from 2D vision, making your production faster and with fewer mistakes. So, if you’re looking to improve how your machines work, 3D vision is the way to go.