Alessio Cocchi
Global Cobot Sales & Marketing Manager, ABB Robotics
28 Nov, 2024.
The landscape of manufacturing and automation is advancing rapidly, and collaborative robots (cobots) are playing a pivotal role. The demand for enhanced flexibility, safety, and cost efficiency has placed cobots at the forefront of industrial automation. The cobot market is projected to grow annually by over 20% between 2024 and 2028, doubling by 20301. In a recent survey, 84% of businesses expressed intentions to adopt or expand robotic automation within the next decade. This reflects the onset of a new era in smart automation, where cobots are enabling companies to innovate, optimize operations, and address emerging challenges.
Market Overview:
The cobot market is set to experience exponential growth, driven by widespread adoption in industries seeking smarter, more agile automation solutions. By 2032, the market is expected to double, with annual growth rates ranging between 20% and 30%3.
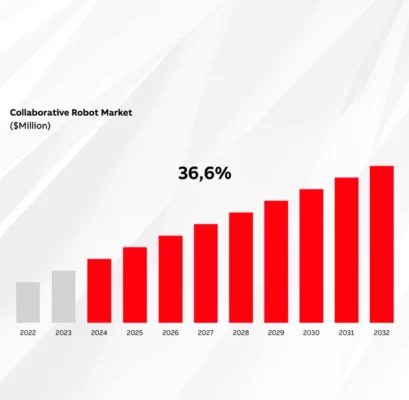
An ABB survey of 1,500 enterprises across Europe, the USA, and China revealed that 84% of businesses plan to introduce or expand robotic automation in the coming years3. This widespread interest highlights the increasing recognition of cobots as essential tools for improving productivity and efficiency in a rapidly changing industrial environment.
Key Trends Driving Cobot Adoption:
1. Labor Shortages:
Workforce challenges, including ageing populations and reduced interest in factory work, are driving cobot adoption. For example, the U.S. faces a gap of 400,000 welders, while Europe reported over 200,000 vacancies in the construction sector in 20202. Cobots address these gaps by performing repetitive, physically demanding tasks, making them a valuable asset for small and large enterprises alike.
2. Individualized Consumer Demands:
The rise of e-commerce has increased consumer expectations for fast delivery, driving the automation of logistics and warehousing. Cobots are ideal for sorting, picking, and packing, providing the flexibility needed to operate in fulfilment centers and adapt to fluctuating consumer demands.
3. Digitalization and AI:
The integration of digital twins and AI into cobots allows manufacturers to optimize operations, predict potential failures, and enhance productivity. Tools like ABB’s RobotStudio enable businesses to simulate, test, and refine processes before real-world deployment, while connected services facilitate remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
4. Economic and Geopolitical Uncertainty:
Manufacturers must adopt flexible automation solutions to address global challenges like supply chain disruptions and reshoring trends. Cobots, with their rapid deployment, compact designs, and short ROI, empower businesses to adapt effectively to these changing conditions.
5. Sustainability:
Sustainability initiatives are reshaping industries, particularly in the shift toward electric vehicles (EVs). Cobots play a key role in supporting environmentally friendly manufacturing processes, such as assembling EV components and handling batteries, while reducing energy consumption and waste.
Emerging Applications of Cobots:
1. Traditional Manufacturing and Assembly:
Cobots are widely used in tasks like material handling, assembly, and screwdriving. Recent advancements have expanded their capabilities to include high-precision operations like polishing, sanding, and small-part assembly, making them indispensable in sectors like automotive and electronics.
2. Welding:
Amid a shortage of skilled welders, cobots have become essential. ABB’s lead-through programming allows welders to guide the robot arm manually, while tools like Wizard Easy Programming simplify cobot setup, enabling their use in high-mix, low-volume production environments.
3. Material Handling and Palletizing:
Cobots enhance efficiency in logistics by performing picking, packing, and palletizing tasks. They complement traditional industrial robots in low-speed production lines or small-batch operations, offering a safer and more ergonomic solution for shared human-robot workspaces.
4. Quality Inspection:
Vision systems and AI have enabled cobots to perform detailed inspections with exceptional accuracy. These capabilities are vital in industries like electronics and automotive, where even minor defects can have significant consequences. ABB’s RobotStudio further enhances quality control by simulating and optimizing inspection processes before deployment.
Increased Adoption Across Industries:
The versatility of cobots has led to their adoption in a growing range of sectors, including healthcare, agriculture, and logistics:
- Healthcare: Cobots like ABB’s YuMi are supporting medical research and treatment development, showcasing their precision and reliability in life sciences.
- Agriculture: Cobots are being used for tasks like harvesting and crop monitoring.
- Niche Industries: From fashion to cosmetics, cobots are finding unique applications, further demonstrating their adaptability.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are also benefiting from cobot integration, leveraging their flexibility to automate processes without significant resource investments.
The video showcases ABB’s dual-arm YuMi robot performing automated pre-analytical lab tasks like pipetting, liquid handling, and microbiological culturing, demonstrating its capabilities for medical applications.
Focus on Safety and Compliance:
Cobots are designed to work safely alongside humans, eliminating the need for external fencing in many applications. Features such as collision detection, redundant safety functions, and certified safety standards ensure that cobots operate securely in diverse environments. Future advancements, including predictive algorithms and real-time monitoring, will further enhance safety and compliance, making cobots even more reliable for shared workspaces.
Conclusion:
The trends outlined in this white paper highlight the transformative impact of cobots on industries worldwide. From addressing labor shortages to enabling sustainable practices and adapting to global challenges, cobots are becoming indispensable tools for modern automation. Their versatility, safety, and efficiency are driving a new era of smart manufacturing, making them a strategic investment for businesses looking to stay competitive in an evolving market.
Access The Complete White Paper
References:
- Interact Analysis. Homepage. Retrieved November 27, 2024, from https://interactanalysis.com/.
- Caldera Manufacturing. Welder Shortage and Its Impact on the Manufacturing Industry. Retrieved November 27, 2024, from https://calderamfg.com/resources/blog/welder-shortage-impact/.
- ABB. ABB Cobot Trends Report. Retrieved November 27, 2024, from https://ebooks.robotics.abb.com/story/abb-cobot-trends-report/page/1.






