Humanoid robots are no longer just ideas from sci-fi movies—they’re here and making a difference in industries like yours. In 2025, these robots are transforming how tasks are done in manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and education. But with so many options out there, choosing the right one for your needs can feel overwhelming. That’s where this guide comes in. You’ll learn about how humanoid robots have evolved, the industries they’re reshaping, and the top models worth considering. Whether you’re looking to boost efficiency or tackle specific challenges, humanoid robots could be the game-changing solution your business has been waiting for.
The History of Humanoid Robots:
Humanoid robots have come a long way. By looking at their history, you’ll see how far they’ve progressed and what they can do for you today.
Early Milestones in Humanoid Robotics:
The term “robot” was first used in Karel Čapek’s 1921 play, R.U.R. (Rossum’s Universal Robots). It introduced the idea of robots working like humans. [1] In 1973, WABOT-1 was built as the world’s first humanoid robot. It could walk, hold objects, and even communicate simple words—groundbreaking for the time. [2]
How Technology Evolved:
Humanoid robots became smarter with advancements in artificial intelligence, sensors, and materials. Now, robots can recognize faces, understand speech, and learn tasks on their own. They’re not just machines—they’re tools that can work alongside you.
Major Breakthroughs You Should Know:
Honda’s ASIMO, released in 2000, set a new standard for humanoid robots. [3] It could run, climb stairs, and interact with humans. Today, the humanoid robot market is booming, growing from $1.02 billion in 2021 to a projected $17.32 billion by 2028. This growth reflects their increasing importance in healthcare, manufacturing, and education. [4]
Understanding their history helps you appreciate what humanoid robots can achieve—and how they can improve your business.
The First Humanoid Robot:
Humanoid robotics began with WABOT-1, created in 1973 at Waseda University in Japan. It was the first full-scale humanoid robot and paved the way for the robots you see today.
What WABOT-1 Could Do:
WABOT-1 could walk, but only on flat surfaces and at a slow pace. Its arms could grip and carry objects, showing early potential for human-like tasks. The robot had a vision system that measured distances and directions, and it could communicate simple phrases in Japanese through an artificial voice system. [5]
Why It Matters to You:
WABOT-1 was a groundbreaking achievement. It showed that robots could mimic basic human functions. This innovation led to modern robots that work faster, smarter, and in more complex environments. Without WABOT-1, the humanoid robots transforming industries today might not exist. [6]
WABOT-1 proves that every big leap in robotics starts with a first step.
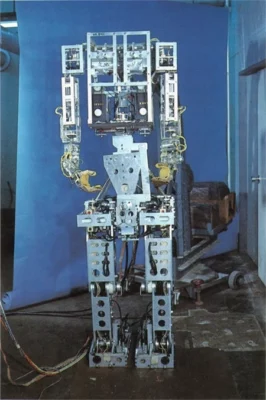
This image depicts WABOT-1, the world’s first full-scale humanoid robot, developed in 1973 by Waseda University. (Image source: Waseda University Humanoid Robotics Institute)
All Humanoid Robot Models:
*We may miss some, but this will be a live blog—if we missed one, let us know in the comments, and we’ll add it!*
1. Advanced Research & General-Purpose:
Ameca (Engineered Arts):
Ameca is a cutting-edge humanoid robot renowned for its highly realistic facial expressions and interactive capabilities. Designed as a platform for advancing human-robot interaction, it features embedded microphones, binocular eye-mounted cameras, a chest camera, and facial recognition software. These components enable Ameca to engage in natural conversations and respond appropriately to human emotions.
Estimated Price: Approximately $100,000-$140,000.
Applications:
- Visitor Interaction and Entertainment: Engaging with guests in venues like museums and exhibitions.
- Research and Development: Providing a versatile platform for studying human-robot interactions and advancing AI technologies.
The video showcases a conversation between Ameca and Azi, two humanoid robots by Engineered Arts, highlighting their advanced expressive and interactive capabilities.
Atlas (Boston Dynamics):
Atlas is a highly agile humanoid robot capable of performing dynamic movements such as running, jumping, and complex maneuvers. Equipped with an advanced control system and state-of-the-art hardware, Atlas demonstrates whole-body dynamic balancing and real-time perception, allowing it to navigate and manipulate objects in complex environments.
Estimated Price: While the exact current price is not publicly disclosed, earlier estimates ranged from $200,000 to $500,000, depending on the model and features.
Applications:
- Disaster Response: Navigating through debris and unstable terrains in disaster-stricken areas, performing search and rescue tasks that are too dangerous for humans.
- Industrial Automation: Assisting in tasks such as material handling and assembly operations in manufacturing settings.
The video features Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robot autonomously moving engine covers between containers and a sequencing dolly, using machine learning and sensor technology to detect, localize, and adapt to changes in its environment in real time.
Phoenix (Sanctuary AI):
Phoenix is a general-purpose humanoid robot developed by Sanctuary AI, designed to perform a wide range of tasks across various industries. Leveraging advanced AI, Phoenix can learn and adapt to new tasks, making it a versatile solution for dynamic environments.
Estimated Price: Pricing details are not publicly available and may vary based on configuration and application.
Applications:
- Retail Assistance: Helping customers with inquiries and managing inventory.
- Logistics Support: Assisting in warehouse operations, including sorting and packaging.
- Security Monitoring: Patrolling premises and identifying potential security threats.
The video showcases Sanctuary AI’s latest advancements in general-purpose AI robotics, highlighting rapid improvements achieved within a year and a major leap in task automation speed.
EVE (1X):
EVE is an AI-powered humanoid robot developed by 1X, capable of learning and performing tasks in various industries. Designed with adaptability in mind, EVE can integrate into different work environments, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Estimated Price: Specific pricing information is not publicly disclosed and may depend on the deployment scale and industry requirements.
Applications:
- Retail: Assisting with customer service and inventory management.
- Logistics: Performing tasks such as sorting, packing, and quality control.
- Security: Monitoring facilities and responding to security incidents.
The video demonstrates 1X’s EVE robots performing multiple autonomous tasks using voice commands, showcasing an AI system that chains simple tasks into complex actions for seamless multi-robot collaboration without teleoperation.
Figure 02 (Figure):
Figure 02 is a humanoid robot developed by Figure, integrating GPT models to combine physical capabilities with advanced conversational AI. This integration allows Figure 02 to perform tasks while engaging in natural language interactions, enhancing human-robot collaboration.
Estimated Price: Pricing details are not publicly available and may vary based on features and deployment scenarios.
Applications:
- Customer Service: Interacting with customers to provide information and assistance.
- Healthcare Support: Assisting medical staff with routine tasks and patient interactions.
- Educational Tools: Serving as an interactive teaching aid in educational institutions.
The video provides an update on Figure’s humanoid robot capabilities, highlighting advancements in OpenAI’s speech-to-speech reasoning technology for improved human-robot interactions.
Service & Hospitality:
Pepper (SoftBank Robotics):
Pepper is a humanoid robot designed to interact with people in a natural and engaging manner. Equipped with advanced AI and emotion recognition capabilities, Pepper can understand and respond to human emotions, adapting its behavior to provide personalized interactions. It features a tablet on its chest for displaying information, making it useful for tasks such as greeting customers, answering questions, or providing directions.
Estimated Price: Approximately $1,00 – $2,000.
Applications:
- Customer Service: Greeting and assisting customers in retail environments.
- Education: Serving as an interactive tool to engage students.
- Healthcare: Providing companionship and information to patients.
The video showcases Pepper, a social humanoid robot by Aldebaran Robotics and SoftBank, highlighting its home companionship features and interactive capabilities.
Promobot (Promobot):
Promobot is a highly customizable humanoid robot designed to function in various service-oriented industries, including hospitality and healthcare. It stands out for its ability to perform a range of tasks, from concierge services to medical assistance, showcasing the multifaceted utility of humanoid robots.
Estimated Price: Varies based on customization.
Applications:
- Concierge Services: Assisting guests in hotels and corporate settings.
- Medical Assistance: Providing information and support in healthcare facilities.
The video showcases Promobot, a retail service robot designed to operate in crowded environments and assist customers by performing tasks such as answering inquiries, promoting offers, and automating routine retail processes to enhance efficiency and customer engagement.
Walker X (UBTECH Robotics):
Walker X is UBTECH’s flagship bipedal humanoid robot. It has 36 high-performance actuators and a range of sensors, enabling it to perform tasks such as walking, climbing stairs, and manipulating objects. Walker X is designed to operate in human environments, providing services like home security, elder care, and smart home control.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Home Security: Monitoring and patrolling residential areas.
- Elder Care: Assisting with daily activities and providing companionship.
- Smart Home Control: Managing connected home devices.
The video showcases UBTECH Robotics’ Walker X, a humanoid robot designed for home and commercial environments, featuring advanced mobility, object manipulation, and interaction capabilities.
Kime (Macco Robotics):
Kime is a humanoid robotic bartender designed to serve food and beverages. It features a robotic head, torso, and two articulating arms that can accurately pour drinks, such as beer, and serve food. Each Kime kiosk is able to dispense 253 items per hour and features a touchscreen and app-enabled ordering, plus a built-in payment system.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Food and Beverage Service: Serving drinks and snacks in venues like bars, restaurants, and events.
These humanoid robots exemplify the integration of advanced robotics into service and hospitality sectors, enhancing customer experiences and operational efficiency.
The video showcases Kime, a humanoid robot by Macco Robotics, designed to safely prepare and serve food and drinks while maintaining hygiene standards.
Logistics & Manufacturing:
Digit (Agility Robotics):
Digit is a bipedal robot designed to navigate human environments and perform tasks such as package handling and unloading trailers. Standing at 5 feet 9 inches and weighing approximately 99.2 pounds, Digit can carry payloads up to 35 pounds. Its design allows it to operate in spaces built for humans without requiring significant modifications.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Logistics: Assisting in warehouses by moving and stacking packages.
- Manufacturing: Transporting materials between workstations.
The video highlights Agility Robotics’ partnership with Amazon, showcasing the humanoid robot Digit being tested to automate repetitive tasks in warehouses, allowing human workers to focus on more complex responsibilities.
Apollo (Apptronik):
Apollo is a general-purpose humanoid robot developed by Apptronik, standing 5 feet 8 inches tall and weighing 160 pounds. It is designed for safe human-robot collaboration in environments like warehouses and manufacturing plants. Apollo can lift up to 55 pounds and operates for up to 4 hours on a single battery charge, with swappable batteries to extend its working time.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Manufacturing: Assisting with assembly line tasks and material handling.
- Logistics: Loading and unloading goods, and transporting items within facilities.
The video introduces Apollo, a humanoid robot developed by Apptronik in collaboration with NASA, designed to assist humans by handling dangerous or undesirable tasks.
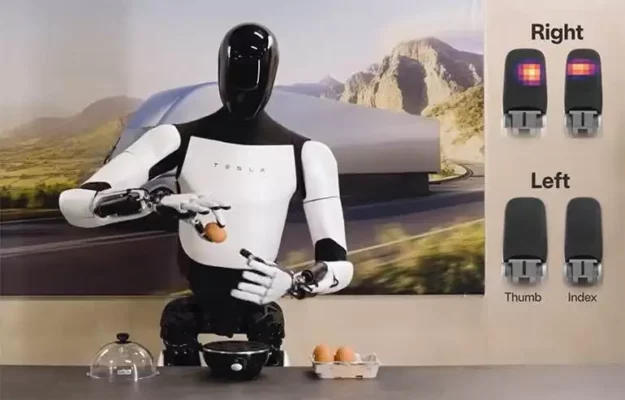
Optimus Gen2 (Tesla):
Optimus Gen2 is Tesla’s humanoid robot designed to perform unsafe, repetitive, or mundane tasks. Standing at 5 feet 8 inches tall and weighing 125 pounds, it features advanced actuators and sensors for precise object manipulation and improved mobility, including a 30% increase in walking speed over its predecessor.
Estimated Price: Projected between $20,000 and $30,000.
Applications:
- Manufacturing: Performing assembly tasks and managing material transport.
- Logistics: Assisting in warehouse operations and inventory management.
The video introduces Tesla’s Optimus Gen 2 humanoid robot, featuring improved actuators, faster and more dexterous hands, increased walking speed, reduced weight, and an articulated neck for enhanced movement and functionality.
Walker S1 (UBTECH Robotics):
Walker S1 is an advanced humanoid robot designed for industrial applications. Standing at 5 feet 6 inches tall and weighing approximately 167.6 pounds, it features 36 high-performance servo joints and a range of sensory systems, including force, vision, hearing, and spatial awareness. Walker S1 is capable of stable walking, flexible and precise handling, and can perform tasks such as visual inspections and equipment handling.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Manufacturing: Conducting visual quality inspections and assembling components.
- Logistics: Handling equipment and transporting materials within industrial settings.
The video showcases UBTECH’s humanoid robot Walker S assisting in NIO’s EV production line by performing repetitive and potentially hazardous workstation tasks, demonstrating its capability to support human workers in industrial settings.
Healthcare:
Sophia (Hanson Robotics):
Sophia is one of the most well-known humanoid robots globally. Developed by Hanson Robotics, it is capable of human-like conversations and emotional expression. Sophia combines advanced AI and facial recognition to interact naturally with humans, making it a popular figure in media and educational spaces.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Media and Public Engagements: Participating in interviews, events, and conferences.
- Education: Demonstrating AI capabilities and human-robot interactions.
The video introduces Sophia, Hanson Robotics’ advanced humanoid robot, showcasing her lifelike expressions, AI-driven interactivity, and ability to engage in natural conversations while learning from her experiences.
Education:
NAO (SoftBank Robotics):
NAO is a compact humanoid robot designed to revolutionize classroom learning by teaching programming, robotics, and STEM concepts. It features 25 degrees of freedom, advanced sensors, and a programmable platform, making it a versatile tool for educators. NAO engages students through interactive storytelling, dance, and project-based learning, making education fun and immersive.
Estimated Price: Approximately $10,000 to $12,000, depending on the configuration and region.
Applications:
- Programming Education: Teaching coding and robotics through hands-on activities.
- Interactive Learning: Engaging students with storytelling, games, and creative projects.
- STEM Curriculum: Supporting science, technology, engineering, and mathematics education.
Pepper (SoftBank Robotics):
Pepper is an interactive humanoid robot that enhances classroom experiences by combining teaching capabilities with emotional recognition. Equipped with AI and a touchscreen display, Pepper can identify students’ emotions and adapt its responses to foster a personalized learning environment. It is widely used in classrooms to facilitate collaborative learning and spark interest in technology.
Estimated Price: Approximately $1,000 – $2,000.
Applications:
- Classroom Assistance: Supporting teachers in delivering lessons and managing activities.
- Interactive Learning: Encouraging participation through games, quizzes, and interactive lessons.
- Emotional Tracking: Adapting teaching strategies based on students’ emotional cues for a tailored approach.
Industrial & Maintenance:
ARMAR-6 (Karlsruhe Institute of Technology):
ARMAR-6 is an advanced humanoid robot engineered for industrial environments. Designed with dexterous hands and powerful actuators, it can perform tasks such as tool handling, object manipulation, and collaborative maintenance alongside humans. Its AI enables task learning, predictive motion planning, and seamless human-robot interaction.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Industrial Maintenance: Assisting in equipment repair and performing routine maintenance tasks.
- Tool Handling: Efficiently managing tools and materials in industrial settings.
- Human Collaboration: Supporting workers by handing over objects and performing complementary tasks.
The video presents ARMAR-6, a humanoid robot by KIT, designed to assist in industrial tasks by using AI to recognize and support human workers.
Underwater Exploration:
OceanOne (Stanford University):
OceanOne is a state-of-the-art humanoid robot designed for deep-sea exploration. Combining a human-like form with advanced sensors and haptic feedback, it allows operators to “feel” underwater objects remotely. Capable of diving up to 1,000 meters, OceanOneK excels in exploring shipwrecks, underwater archaeology, and marine environments, offering precision and care unmatched by traditional robotic systems.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Shipwreck Exploration: Examining and retrieving artifacts from sunken vessels with minimal disturbance.
- Underwater Archaeology: Assisting researchers in documenting and preserving submerged cultural heritage.
- Marine Research: Collecting samples and data from deep-sea ecosystems to support scientific studies.
The video showcases Stanford University’s OceanOne humanoid robot, which uses AI and haptic feedback to explore deep-sea shipwrecks with high precision.
Entertainment & Novelty:
RoboThespian (Engineered Arts):
RoboThespian is an interactive humanoid robot built for performances, public speaking, and educational demonstrations. Featuring expressive gestures, programmable scripts, and multilingual capabilities, it captivates audiences in museums, theaters, and exhibitions. Its modular design allows customization for diverse roles in the entertainment industry.
Estimated Price: Approximately $75,000 – $95,000. (Source: Engineered Arts)
Applications:
- Theatrical Performances: Acting in plays, skits, and scripted productions.
- Public Speaking: Delivering presentations, narrating stories, and engaging with audiences at events.
- Interactive Displays: Attracting and entertaining visitors in museums, science centers, and theme parks.
This video showcases how Kaiserslautern Technical University utilized RoboThespian and Engineered Arts’ software to develop gesture recognition, facial recognition, and automated interactions.
Space Exploration:
Robonaut 2 (NASA and General Motors):
Robonaut 2 is a highly advanced humanoid robot developed by NASA and General Motors to assist astronauts in space. Equipped with dexterous hands and sensors, it is capable of performing intricate tasks in microgravity, such as operating tools, managing equipment, and conducting maintenance. Its modular design allows upgrades for future space missions, enhancing its adaptability for various roles.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Astronaut Assistance: Supporting astronauts with routine and hazardous tasks aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
- Maintenance Tasks: Conducting repairs and inspections in microgravity environments.
- Future Space Missions: Potentially aiding in deep-space exploration and extraterrestrial habitat construction.
The video highlights NASA’s Robonaut 2, an advanced humanoid robot designed to assist in deep space missions, planetary exploration, and tasks aboard the International Space Station to pave the way for future human space exploration.
Vyommitra (Indian Space Research Organisation):
Vyommitra is a humanoid robot developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) as part of the Gaganyaan human spaceflight program. Designed to resemble a female astronaut, Vyommitra can perform tasks such as monitoring environmental parameters, interacting with spacecraft systems, and relaying mission data. It serves as a precursor for future human spaceflights.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Spacecraft Operations: Assisting in operating spacecraft systems and conducting experiments during missions.
- Data Monitoring: Providing real-time updates on environmental and system parameters.
- Human Spaceflight Preparations: Testing systems and environments for future crewed missions.
The video by Times of India discusses ISRO’s upcoming Gaganyaan mission, featuring “Vyommitra,” a female humanoid robot, which will be part of an unmanned trial spaceflight planned for October.
Regional Innovations:
Surena IV (University of Tehran):
Surena IV is a humanoid robot developed by the University of Tehran, showcasing advanced capabilities such as walking, writing, and handling tools. It features 43 degrees of freedom, facial recognition, and speech capabilities, making it suitable for research and practical applications. Its design represents a significant step in robotics innovation in the Middle East.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Research and Development: Serving as a platform for robotics and AI advancements.
- Industrial Tasks: Performing tool usage and object manipulation in controlled environments.
- Public Demonstrations: Showcasing technological achievements in regional and global exhibitions.
The video showcases the development of Surena IV, an advanced humanoid robot created by University of Tehran researchers, highlighting its improved design and capabilities over previous generations.
Emerging Innovations:
Pudu D9 (Pudu Robotics):
Pudu D9 is a full-sized bipedal humanoid robot developed for service applications, including ground cleaning and facility maintenance. Equipped with autonomous navigation and advanced sensory systems, it efficiently handles large-scale cleaning tasks in commercial and public spaces.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed.
Applications:
- Facility Maintenance: Performing floor cleaning in malls, airports, and offices.
- Service Support: Assisting in managing tasks such as sanitation in busy environments.
- Public Interaction: Acting as a multifunctional service robot in customer-facing roles.
The video introduces the PUDU D9, Pudu Robotics’ first full-sized bipedal humanoid robot, designed for practical assistance with advanced mobility, manipulation, and interaction capabilities.
Unitree G1 (Unitree Robotics):
Unitree G1 is a humanoid robot recognized for its affordability and mobility. Designed for accessibility, it combines a compact build with advanced features like dynamic motion control, making it a versatile choice for education, research, and light industrial tasks.
Estimated Price: Approximately $3,000 to $5,000, making it one of the most affordable humanoid robots available.
Applications:
- Education: Teaching robotics and programming in academic settings.
- Research: Serving as a cost-effective platform for experimenting with AI and robotics.
- Light Industrial Tasks: Assisting with small-scale material handling and inspections.
This CNET video provides a hands-on look at the Unitree G1 humanoid robot and Go2 Canine robots at CES 2025, showcasing their capabilities and control mechanisms.
HumanPlus (Stanford University):
HumanPlus is a cutting-edge prototype robot from Stanford University, designed to mimic human movements through advanced motion capture and machine learning. It can learn complex tasks, such as playing table tennis and the piano, showcasing the potential for robots to replicate intricate human skills.
Estimated Price: Not publicly disclosed, as it remains a prototype.
Applications:
- Skill Replication: Learning and performing precise tasks like musical performance and sports.
- Human-Robot Collaboration: Enhancing cooperative tasks requiring fine motor skills.
- Research and Development: Pioneering the integration of robotics and machine learning in skill acquisition.
The video showcases HumanPlus, a humanoid robot autonomously folding a piece of clothing using its learned motion skills and egocentric vision, demonstrating its ability to perform complex household tasks with precision and adaptability.
Why Watch Tesla’s Optimus Gen2?
Mass Production Focus:
Tesla’s Optimus Gen2 is designed with mass production in mind, aiming to make humanoid robots accessible on a large scale. Elon Musk has indicated that Optimus could become “the biggest product ever of any kind,” highlighting its potential impact. [7]
Integration with Tesla’s AI:
Optimus Gen2 leverages Tesla’s advanced AI systems, including technologies developed for autonomous driving. This integration allows the robot to adapt and function efficiently in diverse environments, enhancing its versatility across various applications.
Practical Applications:
Designed as a versatile general-purpose robot, Optimus Gen2 has been demonstrated performing tasks such as lifting objects, assembling parts, and working alongside humans in factories. This flexibility sets it apart from many specialized humanoid robots.
Scalability:
Backed by Tesla’s substantial infrastructure and resources, Optimus Gen2 has the potential to reach a scale that few competitors can match. This scalability could significantly lower costs and lead to wider adoption of humanoid robots in various industries.
Elon Musk’s Vision:
With Tesla’s track record of disrupting industries, the company’s commitment to humanoid robotics is a strong indicator of its transformative potential. Musk has stated that Optimus could be “the biggest product ever of any kind,” underscoring its anticipated significance.
Other Contenders to Watch Out For:
While Tesla’s Optimus Gen2 is making waves, you should keep an eye on these other impressive robots that are redefining the possibilities of humanoid robotics:
Sanctuary AI’s Phoenix:
Phoenix is built for versatility. It’s a general-purpose robot designed to take on jobs across industries. Standing 5 feet 7 inches tall and weighing 155 pounds, it can lift up to 55 pounds. Thanks to its advanced AI system, called Carbon™, Phoenix can quickly learn and adapt to new tasks, giving you a reliable tool for work environments.
Engineered Arts’ Ameca:
Ameca stands out for its lifelike expressions and ability to interact naturally with people. Designed as a testbed for AI, it’s modular, meaning you can easily upgrade its hardware or software. This makes it ideal if you want a robot for customer interaction or even entertainment.
Boston Dynamics’ Atlas:
Atlas is the athlete of humanoid robots. It can run, jump, and perform complex movements with ease. Its real-time perception and advanced control systems make it perfect for navigating challenging spaces or handling objects. If you’re looking for a robot with agility, Atlas is a standout.
These robots each have unique strengths. But if scalability, affordability, and versatility are your priorities, Optimus Gen2 could still be the best choice for your needs.
Technical Components & Innovations:
Humanoid robots are packed with advanced technology that helps them work efficiently and adapt to your needs. Let’s break down the key components that make these robots so powerful.
AI & Machine Learning Integration:
Thanks to AI and machine learning, humanoid robots can recognize faces, understand speech, and even learn from experience. They get better over time by analyzing data and adjusting their actions. For example, robots like Ameca use AI to have natural conversations and respond to emotions. This makes them useful in customer service, healthcare, and more.
Hardware Innovations:
Robots today are built with stronger, lighter materials that help them move smoothly and last longer. Sensors in their eyes and hands allow them to detect objects and people with precision. Actuators—like robotic muscles—give them human-like movement, while better batteries mean they can work longer without needing a recharge. Robots like Atlas from Boston Dynamics use these advancements to run, jump, and lift objects safely.
Software Capabilities:
Your humanoid robot connects to the cloud for updates and remote control. This keeps it up to date with the latest improvements. Security features protect your data, ensuring safe interactions. Robots like Tesla’s Optimus Gen2 rely on advanced software to perform tasks accurately and securely.
These innovations are why humanoid robots are becoming smarter, safer, and more useful in everyday life.
Conclusion:
Humanoid robots are no longer a thing of the future—they’re here and ready to help your business. Whether you work in manufacturing, healthcare, retail, or education, these robots can take on tasks that improve efficiency and reduce costs. With smarter AI, better materials, and advanced software, they are becoming easier to use and more reliable. Choosing the right robot can feel overwhelming, but understanding their benefits makes it easier. As technology improves and prices drop, now is the perfect time to explore how humanoid robots can give your business a competitive edge.
References:
- Kawasaki Robotics. (n.d.). Humanoid Robotics: Key Milestones in the History of Robots. Retrieved on January 16, 2025, from https://kawasakirobotics.com/asia-oceania/blog/2101-01/
- Conomis AI. (n.d.). Humanoid Robots: Breakthroughs in Human Companionship. Retrieved on January 16, 2025, from https://conomis.ai/humanoid-robots-breakthroughs-human-companionship/?
- How We Get to Next. (n.d.). A History of Humanoids. Retrieved on January 16, 2025, from https://www.howwegettonext.com/a-history-of-humanoids/?
- Latent View. (n.d.). The Rise of Humanoid Robots: Transforming Industries. Retrieved on January 16, 2025, from https://www.latentview.com/blog/the-rise-of-humanoid-robots/?
- Waseda University Humanoid Robotics Institute. (n.d.). Wabot 1: The first humanoid robot. Retrieved on January 16, 2025, from https://www.humanoid.waseda.ac.jp/booklet/kato_2.html?
- Kalil, M. (n.d.). Japan’s humanoid robots. Retrieved on January 16, 2025, from https://mikekalil.com/blog/japan-humanoid-robots/?






